 "QUANTUM SHOT" #475 "QUANTUM SHOT" #475
Link -- Article by M. Christian of "Meine Kleine Fabrik" and Avi Abrams
Fulfilling numerous requests from our readers, here is a page documenting the history of huge airplanes, in a visually striking and wondrous manner:
Flying on Gigantic Wings
For a few thousand years the biggest things in the skies were only in our imaginations, flying figments of myth and fable: the Roc from Sinbad’s tales, the Garuda bird from the Mahabharata, the Thunderbird from North America, the Brazilian Blue Crow, and other high-flying nightmares or soaring benevolent gods and spirits.

(art by Harry Grant Dart, All-Story ca. 1900)
But then a few very clever, and rather persistent, folks got tired of only dreaming. With great inventiveness, they wanted to see what was actually above the clouds. They sought to create something as wondrously big, or nightmarishly immense, as those birds of myth and legend.

(image credit: retro-futurismus)
Talking about big planes is very much like talking about who should get the credit for man’s first flight –- it all depends on who you talk to. As the brilliant James Burke has pointed out, inventors rarely create something from nothing –- their successes are often the result of combining the partial successes, or learning from the downright failures, of other inventors. In some cases, it's just pure dumb luck.
Sputtering, Creaking, Terrifying Monsters
The Wright Brothers are often given most of the recognition for the first powered flight but Gustave Whitehead, Alexander Feodorovich Mozhaiski, Clement Ader, and many others should get a share of the fame, too. Whoever is responsible, it wasn’t long before the skies were full of sputtering, creaking, and – for the most part – very unreliable aeronautical devices.
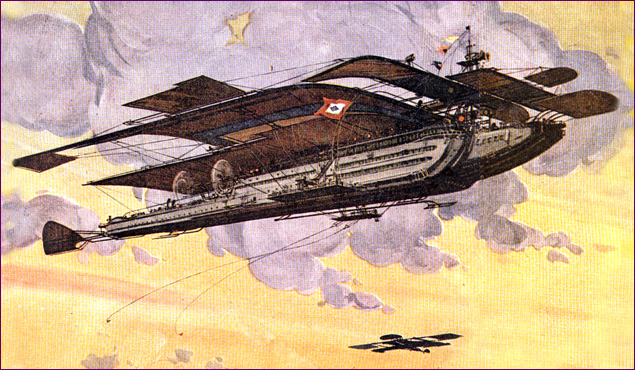
(futuristic art by Harry Grant Dart)
It took the first world war to change aircraft from a killing and maiming hobby for the rich to a killing and maiming war machine. War helped advance the science of flight and necessitated bigger planes.
One monster plane of that time was Igor Sikorsky's Ilya Murometz, a huge improvement over his legendary Russky Vitaz, the first four engine aircraft. But the Ilya Murometz didn't begin as a beast of the skies. Originally designed as a luxurious passenger liner featuring electric lighting, heat, a bathroom, and even a glass floor, the bomber must have been amusing as well as terrifying to its wealthy passengers.
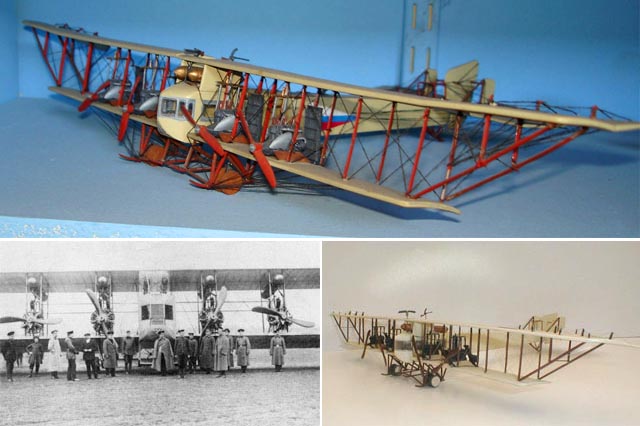
(images credit: histarmar.com.ar)
Another iteration of such approach was Tupolev ANT-20 "Maxim Gorky":

And a really huge Russian monster plane from the early 1930s: Ka-7 (more info), named after engineer Kalinin, not the famous political figure.

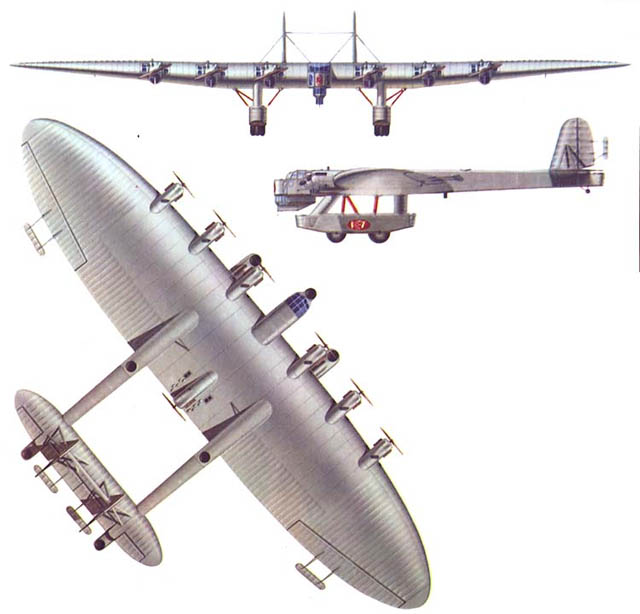
(images via Modelist-Konstruktor, 1989)
Art and Elegance Between Wars
In the years between wars, airplanes kept getting bigger. Outrageous concepts like Norman Bel Geddes Airliner Number 4 appeared, featuring 9 decks of luxury hotel accommodation, bars and engine rooms:


It would sleep 606 passenger in comfort, easily bringing them across Atlantic. More images and info about Bel Geddes fantastic dream planes are here. It seems to be a logical development of 1910s British Airliner of the Future:
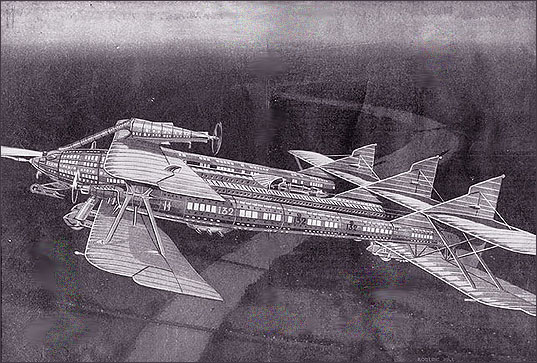
(image via)
Don't miss also this "Freak of the Month" concept from Modern Mechanics, 1931:

(image credit: modernmechanix)
But let us get back from aviation dreams to reality. Take the elegant Handley Page HP42, for instance: a four-engined beauty with an impressive track record of no crashes while being used as an airliner -- which gives you an idea of how safe it was to fly back then.
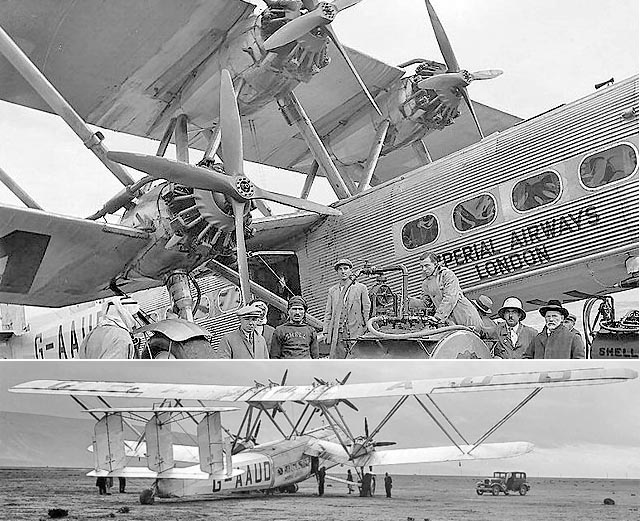


(images via)
One of the larger and more beautiful aircraft in the next few decades was the awesome 1936 Boeing Stratoliner. Unfairly called a ‘whale’ because of its chubbiness, the plane was not only huge but also state of the art; today we enjoy flying in pressurized comfort because of technology premiered in the silver flying fish of the Stratoliner.

Another aircraft both immense and legendary - The H-4 Hercules. Arguably the standard by which “huge aircraft” are measured –- as well as how "completely screwed up" is defined. Its one and only flight was in 1947, where it flew for around a mile, reaching altitude of 70 feet. Originally planned as the ultimate military transport, it is more commonly known as its hated -- at least by its creator Howard Hughes -- moniker, the Spruce Goose.
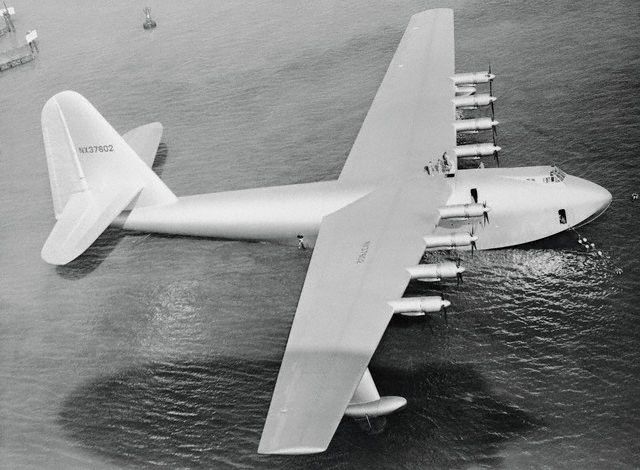


(image credit: Bettman/CORBIS)
The aircraft had originally been ordered by the US government during World War II as a giant cargo plane for the armed troops and tanks. Howard Hughes's creation was the world's largest plane at the time and is still the largest flying boat ever built. It also holds records for the largest wingspan at 97.5 meters, tallest airplane at 24.2 meters, and the largest aircraft ever made from wood.

Nazi's Ugly Brute
Art and elegance may have been one of the early fatalities in the second world war, but striving to have the biggest (anything) certainly wasn’t.

To call the Messerschmitt Me 321 big is like calling 1939 to 1945 unpleasant. Created originally as a glider, the Gigant could haul an insanely large amount of cargo. And an insane bunch of soldiers: 130 plus hardware ... 23 tons of hardware.

(images via)
Because the Gigant was so huge, getting the damned thing into the air was, at best, problematic. First it was towed up with a pair of Heinkel 111 bombers, which was alternatively unsuccessful or disastrous. Then they tried fusing two 111s together to make a Frankenstein’s monster of a machine –- almost as bestial as the Gigant itself. Finally the Luftwaffe stuck engines on the Me321, which made an ugly brute even uglier but at least it got off the ground.
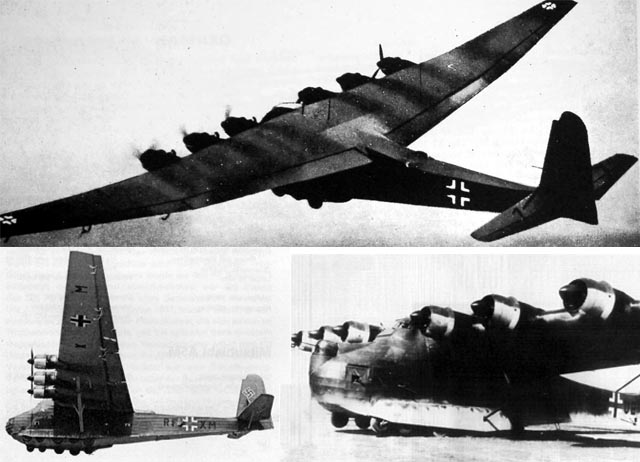

Heavy Bombers of the (Potential) Doomsday
On the other side of the war was an eagle, a silvery steel bird of prey: the huge and beautiful B-29 Superfortress. Although getting the immense B-29 up to its ceiling of 40,000 feet was a struggle, once it got up there nothing could reach it or, at 350 mph, catch it. Even if something managed to come close to it, its formidable defenses could cut any threat to shreds. Featuring many impressive advancements, and some frustrating problems, the plane was kept on active duty long into the Korean war.
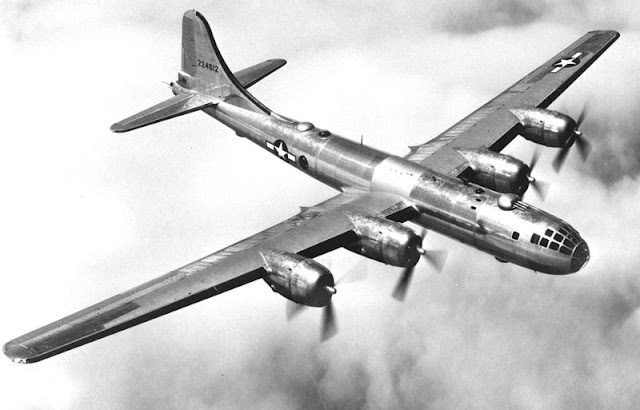

(image via)
With the advent of jet power, aircraft designers began to think really big. Think of your average doomsday film and you immediately picture the roaring ascent of smoke-blasting, eight-engined, B-52 bombers. But before B-52 there was another huge American bomber: Convair B-36 "Peacemaker":





(images via)
Like the B-29, the B-52 "Stratofortress" was an aeronautical powerhouse, a heavy-lifting behemoth. And like the B-52, it was kept in service until … well, they are still being used today.

(image source: US Air Force)
Heavy bombers transforming into LEGO pieces in the minds of dazed Cold War engineers:
Arthur Kimes writes to us: "Soviets also proposed to stick together a bunch of big airplanes to make a REALLY huge one. Kind of like a Lego dream come true: In the early-mid 1950s the USAF had a plan to link 3 B-36s (wingtip to wingtip) to have a extended range delivery system. When this behemoth got close enough to the Soviet Union each would drop off a parasite fighter-bomber (probably the F-92 - which also was never built) and the released FBs would make a high-speed dash and drop a bomb on their targets. The B-36s would split up and return, the F-92s would have to try and find a friendly airfield in Turkey or something like that."

(image source: TM, 1975)
"When you consider the B-36 is still the largest bomber ever built, the idea of 3 of them flying joined at the wingtips is astounding."
The Ugliest Airplane Ever Built?
The Aero Spacelines Super Guppy looks more like a prop from a Japanese monster movie than a real airplane. The Guppy is also high on the irony meter as it was mostly used to haul nearly-completed components -- of other airplanes.
|